ONSET (Optimizer for logic Networks Supported by Extension of Transduction method) is a powerful program for simplifying combinational logic circuits. It has the following functions.
The execution time limit here denotes the used CPU time in the workstation version while it denotes the actual elapsed time (including waiting time for command entry) in the MS-DOS version.
Character strings specified in argument are used in the order of $1, $2, $3, ... by the ONSET command script.
ONSET operation depends on how the commands listed in Section 8.4 are provided. In PARTHENON, ONSET is usually called from OPT_MAP. In such a case, ONSET proceeds in the following order:
If the script file of a:\par\com\onset.dir\b2n_area.scr contains the following:
verbose $2 in_blif $1.bli area.scr out_nld $1.nldand if ONSET is started by:
A>onset -f a:\par\com\onset.dir\b2n_area.scr ALU4 onthen, the following command script is executed:
verbose on ........ Specifies information display mode in_blif ALU4.bli ... Inputs multi-level logic circuit ALU4.bli in the BLI format area.scr ........... Calls the script file for circuit simplification out_nld ALU4.nld ... Outputs netlist ALU4.nld in the NLD formatThe script file area.scr is called in the command script. That is, the command scripts can be nested.
The script file name specified in the '-f' option must be specified by the correct full path name, such that it can be referenced from the current directory. On the other hand, if a script file is called in the interactive mode or from another script, the normal path name (as mentioned above) and a path name relative to %PARTHENON%\com\onset.dir are both searched for the file to be executed (with higher priority given to the former). If area.scr does not exist in the current directory in the above example, a:\par\com\onset.dir\area.scr is executed.
Practical example of using ONSET in the interactive mode
An example of executing commands in the interactive mode is given below. This example assumes that file ALU4.bli in the BLIF format has already been created in the current directory by the blif command of OPT_MAP.
A>onset ONSET> in_blif ALU4.bli .... (1) Inputs multi-level logic circuit ALU4.bli in the BLIF format ONSET> print_cost .......... (2) Displays various circuit cost information details ONSET> prefact ............. (3) Performs factorization and local simplification ONSET> sgs ................. (4) Performs simplification by replacing gates ONSET> condis .............. (5) Performs simplification by adding or deleting connections ONSET> sgs ................. (6) Performs simplification by replacing gates ONSET> gm .................. (7) Performs simplification by merging gates ONSET> condisa ............. (8) Performs simplification by adding or deleting connections ONSET> cpb 4 ............... (9) Re-synthesizes critical paths ONSET> map ................ (10) Maps to a circuit with composite gates ONSET> sgsm ............... (11) Performs simplification of the circuit with composite gates ONSET> constant ........... (12) Treats constant output terminals ONSET> print_cost ......... (13) Displays various circuit cost information details ONSET> out_nld ALU4.nld .. (14) Outputs netlist ALU4.nld in the NLD format ONSET> !dir ............... (15) Executes DOS command dir ONSET> bye ................ (16) Terminates ONSET A>
The above yields a netlist in the NLD format of a multistage logic circuit after a series of simplification steps.
Figure 8.1 illustrates the various commands provided by ONSET and how they fit into the various steps of ONSET processing. The above example follows the flow in bold lines in the figure. However, the order of execution of various commands for simplification in items (3) to (8) and the number of repetitions can be arbitrary. A key point in simplification is the selection of an appropriate order for the commands and an appropriate number of repetitions according to the characteristics of the given logic circuit.
<Fig. 8.1> ONSET process flow
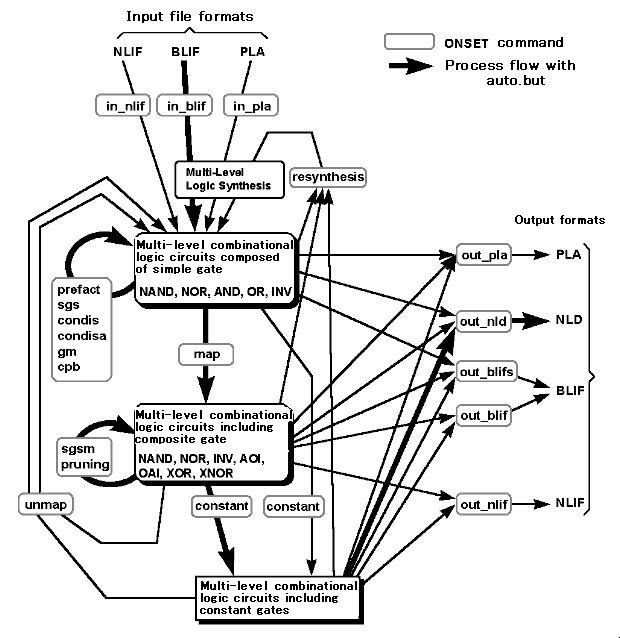
Details of logic circuit simplification are not provided here. For details, refer to documents on the transduction method.
Considerable time may be required in executing logic circuit simplification commands, logic function and netlist input commands, even for a relatively small circuit, depending on the nature of the given logic circuit.
The script examples 'area.scr' and 'delay.scr' in %PARTHENON%\com\onset.dir are expected to perform simplification with priority on area and delay time respectively, based on experience in designing numerous circuits. Changing the order or the number of repetitions of simplification commands in these scripts may yield better results depending on the given circuit.
If you want to execute various simplification commands after the execution of the 'map' command, you should first execute the 'unmap' command to convert the circuit back into one consisting of simple gates only. Repeating this may further simplify some circuits.
The 'resynthesis' command abandons all the previous circuit structure and re-synthesizes a circuit anew from the logic functions to be satisfied by the output terminals. This may greatly simplify some circuits. However, considerable execution time may be required depending on the characteristics of the circuit (logic functions).
Correct operation of ONSET cannot be assured if looped combinational logical circuits are included.
Table 8.1 provides a list of ONSET commands. The details on each command can be displayed with the on-line help function, which can be initiated by the 'help' command (MS-DOS's more.com is called from ONSET).
<Table 8.1> List of ONSET Commands
| Logic function or netlist input commands | |
| in_pla file_name | Input logic functions in PLA format and synthesizes initial multi-level logic circuit |
| in_nlif file_name | Inputs netlist in NLIF format |
| in_bilif file_name | Inputs netlist in BLIF format |
| Logic function or netlist output commands | |
| out_pla [file_name] | Outputs logic function in PLA format (to standard output if file name is omitted) |
| out_nlif [file_name] | Outputs netlist in NFIF format (to standard output if file name is omitted) |
| out_blif [file_name] | Outputs netlist in BLIF format from circuit with composite gates (to standard output if file name is omitted) |
| out_blifs [file_name] | Outputs netlist in BLIF format from circuit with decomposed gates (to standard output if file name is omitted) |
| out_nld [file_name] | Outputs netlist in NLD format (to standard output if file name is omitted) |
| Logic circuit simplification commands | |
| prefact | Performs factorization and local simplification |
| sgs | Performs simplification by replacing gates |
| condis | Performs simplification by adding or deleting connections (except for AND and OR gates) |
| condisa | Performs simplification by adding or deleting connections (applicable to all gates) |
| gm | Performs simplification by merging connections |
| cpb[n] | Re-synthesizes critical paths (n : Index representing the scope of re-synthesis. It ranges from 1 to 4 and the default is 1.The larger the index, the larger the scope of re-synthesis) |
| map | Maps to a logic circuit with composite gates. |
| sgsm | Performs simplification by replacing gates of a circuit including composite gates |
| pruning | Removes redundant connections and gates using MSPF (Maximum Set of Permissible Function) |
| constant | Synthesizes constant output terminals with redundant gates |
| unmap | Converts the circuit after map execution to a circuit consisting of only basic gates by disassembling composite gates |
| resynthesis | Re-synthesize the whole circuit from expressions of output functions |
| Display commands | |
| print_names | Displays module name, input terminal names, output terminal names, and ID numbers of corresponding output gates |
| print_cost | Displays various circuit cost information details (calculated using MCNC lib2 constant) |
| print_level | Displays gate ID numbers for each logic stage |
| print_gate [n] | Displays type and connection information of the gate of specified ID number (all gates if not specified) |
| print_givenf [name] | Displays permissible functions, in sum-of-product logic expression, to be achieved for specified output terminals (all output terminal if not specified) |
| print_givenf_cube [name] | Displays permissible functions, in cube format, to be achieved for specified output terminals (all output terminals if not specified) |
| print_outf [n] | Displays logic function, in sum-of-product logical expression, achieved by output gate of specified ID number (all output gates if not specified) |
| print_outf_cube [n] | Displays logic function, in cube format, achieved by output gate of specified ID number (all output gates if not specified) |
| print_func [n] | Displays logic function, in sum-of-product logical expression, achieved by gate of specified ID number (all gates if not specified) |
| print_func_cube [n] | Displays logic function, in cube format, achieved by gate of specified ID number (all gates if not specified) |
| print_cspf [n] | Displays CSPF (Compatible Set of Permissible Functions), in sum- of-product logic expression, calculated for specified ID number gate (all gates if not specified) and for connection net which is input to that gate |
| print_cspf_cube [n] | Displays CSPF (Compatible Set of Permissible Functions), in cube format, calculated for specified ID number gate (all gates if not specified) and for connection net which is input to that gate |
| print_args | Displays arguments (parameters at start) |
| Other commands | |
| name new_name | Changes circuit module name to new_name |
| verbose [{on|off}] | If 'on' is set, displays the same information as one displayed by print_cost command each time circuit is changed. If 'off ' no such information is displayed. |
| help[{command_type | command_name}] | Displays description of commands( text is found in doc.dir\onset.dir ) |
| bye | Terminates ONSET |
| echo string | Displays string as it is |
| file_name | Executes specified file as script file (directory or com\opt_map.dir is searched for file_name and file is executed) |
| !string | Transfers string to external shell (command.com in the case of MS-DOS) and executes it (execution of external command) |
| (Notes) Script file format | |
| command | Writes any one command in a line |
| command;comment | Ignores statement after ' ; ' |
| ;comment | Comment line |
| file_name | Calls and executes other script files (nesting allowed) |
| !string | Executes external commands |
' $ ' and ' $0 ' are replaced with set module names.
' $1 ',' $2 ',........ are replaced with respective parameters specified at start.
'\' is used as an escape character.